Sociodemographic and Clinical Profile of Patients with Anorectal Diseases in A Tertiary Care Hospital of North India: A Cross Sectional Observational Study
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Healthcare specialists encounter a spectrum of anorectal diseases which range from benign conditions such as hemorrhoids to more serious conditions such as malignancy. The present study aimed to study the prevalence and clinical presentation of anorectal disorders in population visiting a tertiary care centre.
Materials and Methods: The current investigation took place from August 2019 to February 2020 and was an observational cross-sectional study. All patients who complained of having anorectal issues were enrolled in the trial. After receiving their informed consent, they underwent an in-depth interview utilising a pretested structured questionnaire that centred on socio-demographic characteristics, a full physical examination, including a digital rectal examination and proctoscopy, and a detailed clinical history. For several factors, frequencies were computed. A p value of 0.05 was considered significant after data analysis.
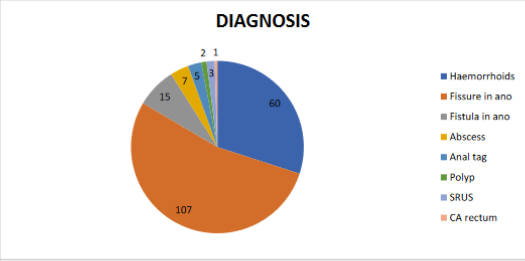
Results: Of the total 200 cases, majority were males (n=143).A total of 97 were Fissure in ano, 60 are Hemorrhoids, rest were Abscess, Fistula, Solitary rectal ulcer syndrome (SRUS). Common disease in both males and females was Fissure in ano, followed by Haemorrhoids. Majority of the subjects complained of pain (n=133) followed by bleeding, discharge and constipation.
Conclusion: Unhealthy life style habits are causative factors leading to Anorectal disorders.
Article Details
References
Goldstein ET, outcomes of anorectal disease in a health maintenance setting, the need for colorectal surgeons, Dis Colon Rectum 1996;39(11):1193 - 1198
Sneider, EB, Maykel JA. Diagnosis and management of symptomatic hemorrhoids, SurgClin North Am 2010;90(1):17 - 32
Grucela A, Salinas H, Khaitov S, et al, Prospective analysis of clinician accuracy in the diagnosis of benign anal pathology: comparison across specialties and years of experience. Diseases of colon rectum. 2010;53(1):47 - 52
Berman L, Israel GM, McCarthy SM, Weinreb JC, Longo WE. Utility of magnetic resonance imaging in Anorectal disease. World J Gastroenterology 2007 :3153 - 3158
Nelson H, Cima RR. Anus. Sabiston textbook of surgery, 18th edition
Emeka Ray-Offor , Solomon Amadi, Hemorrhoidal disease: Predilection sites, pattern of presentation, and treatment: Ann Afr Med, Jan-Mar 2019;18(1):12-16.
Dr Pradeep Kumar J et al ,Our Experience with Doppler Guided Haemorrhoidal Artery Ligation in Treating 100 Cases of Symptomatic Grade 3 and Grade 4 Haemorrhoidal Diseases- 1 Year Follow Up JMSCR : May 2019 ;Volume 07 Issue 05 :534-540
Robert Tessler et al, Rectal bleeding and implications for surgical care in Nepal Journal of Surgical Research Volume 197, Issue 1, July 2015, Pages 12-17.
IsmaelH.R Mohamed A. Akl , et al,Tolmetin sodium-loaded thermosensitive mucoadhesive liquid suppositories for rectal delivery; strategy to overcome oral delivery drawbacks: Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, Volume 45, 2019 - Issue 2 ,
Pigot et al, Defecation Disorders: A French Population Survey:Diseases of the Colon & Rectum: February 2006 - Volume 49 - Issue 2 - p 219-227 doi: 10.1007/s10350-005-0249-8
Ravindranath GG, Rahul BG. Prevalence and risk factors of hemorrhoids: a study in a semi-urban centre. Int Surg J 2018;5:496-9.
Khan RM, Itrat M, Ansari AH, Zulkifle M. A study on associated risk factors of haemorrhoids. J Biol Sci Opinion. 2015;3(1):36-8.
B.A.Sikirov Primary Constipation :An underlying Mechanism .Med Hypothesis 1989; Feb ;28(2):71-3
Sikirov, D. Comparison of Straining During Defecation in Three Positions: Results and Implications for Human Health .Dig Dis Sci2003; 48:1201-1205.