Evaluation of Effect on Hemodynamic Parameters of Supplementation of Low Dose Intravenous Dexmedetomidine on Characteristics of Spinal Anaesthesia with Hyperbaric Bupivacaine
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: The most frequent symptom leading patients to seek medical attention is pain. Not only a sensory modality, but also an actual experience, is pain. The way a person reacts to pain can vary greatly between individuals as well as within the same person over time.
Aim and Objective: The purpose of the current study was to investigate how the addition of low dosage intravenous dexmedetomidine affected the features of spinal anaesthesia with hyperbaric bupivacaine.
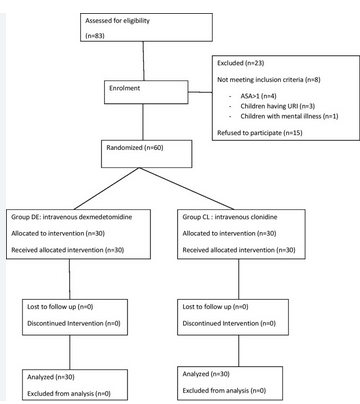
Methodology: The present study was carried out at Santosh Medical College & Hospital, Ghaziabad in 50 patients of age group 18-65 years & weight 30- 70 kg of both sexes belonging to ASA l & ll undergoing lower abdominal & lower limb surgeries.
Result: There were 18 females and 32 males in the study population. In the groups D, the mean age was 36.28 ± 12.70 years, while in the groups C, it was 39.36 ± 13.43 years. There was no statistically significant intergroup difference in heart rate, SBP, DBP, and MAP.
Conclusion: SBP, DBP, and MAP did not differ significantly across groups. Therefore, it was determined by the study that hemodynamic changes are not statistically significant.
Article Details
References
Mighty things from small beginning grow’ John Dryen (1631-1700) Annus mirabilis. Anaesthesia. 1999;54(9):823-825.
Stappendal R., Weber E.W., Benraad B., Van Limbeek J., Dirksen R., itching after intrathecal morphine, incidence and treatment, eur j anaesthesiol 2000;17:616-21.
Kanazi GE, Aouad MT, Jabbour-Khoury SI, Al Jazzar MD,Alameddine MM, Al-Yaman R, Bulbul M, Baraka AS. Effect of low-dose dexmedetomidine or clonidine on the characteristics of bupivacaine spinal block. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2006;50:222–7
Al-Mustafa MM, Abu-Halaweh SA, Aloweidi AS, Murshidi MM, Ammari BA, Awwad ZM, Al-Edwan GM, Ramsay MA. Effect of dexmedetomidine added to spinal bupivacaine for urological procedures. Saudi Med J 2009;30:365–70
Eid H, Shafie M, Youssef H. Dose-related prolongation of hyperbaric bupivacaine spinal anesthesia by dexmedetomidine. Ain Shams J Anesthesiology 2011;4:83–95
Parkhouse J, Lambrechts W, Simpson BRL- The incidence of postoperative pain. Br J Anaesth 1961;33:345-353
Gupta R, Bogra J, Verma R, Kohli M, Kushwaha JK, Kumar S. Dexmedetomidine as an intrathecal adjuvant for postoperative analgesia. Indian J Anaesth 2011;55:347–51
Shukla D, Verma A, Agarwal A, Pandey HD, Tyagi C. Comparative study of intrathecal dexmedetomidine with intrathecal magnesium sulfate used as adjuvants to bupivacaine. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 2011;27:495–9
Bonica JJ, Yaksh T, Liebeskind JC, Pechick RN, De Paulis A; Biochemistry and modulation of nociception and pain. Philadelphia; Lea and Febiger 1990;95-121.
Corning J.L.N.Y. Med. J. 1885;42:483(reprinted in ‘Classical File’, Survey of Anaesthesiology 1960;4:332)
Lund PC. Principles and Practice of Spinal Anesthesia. Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas, 1971.
Deutsh. Zeit. F. Chir. 1899;51:361(translated and reprinted in ‘Classical File’, Bier Survey of Anesthesiology 1962;6:352).
SS Harsoor, D Devika Rani, Bhavana Yalamuru, K Sudheesh, SS Nethra. Effect of supplementation of low dose intravenous dexmedetomidine on characteristics of spinal anaesthesia with hyperbaric bupivacaine. Indian J Anaesth 2013;57:265-269
Anbarasu Annamalai, Sanjeev Singh, Arti Singh and Deigheidy Ehab Mahrous. Can Intravenous Dexmedetomidine Prolong Bupivacaine Intrathecal Spinal Anesthesia? J Anesth Clin Res 2013;4:372.
Al-Ghanem SM, Massad IM, Al-Mustafa MM, Al- Zaben KR, Qudaisat IY, Qatawneh AM, et al. Effect of adding dexmedetomidine versus fentanyl to intrathecal bupivacaine on spinal block characteristics in gynaecological procedures: A double blind controlled study. Americal Journal of Applied Sciences 2009;6:882-887.
Lugo VW, Gomez IA, Cisneros, Corral R, Martinez, Gallegos N. Intravenous dexmedetomidine versus intravenous clonidine to prolong bupivacaine spinal anaesthesia. A double blind study. Anestesia en Mexico 2007;19:143‑6
Revill SI, Robinson JO: The reliability of linear analogue for evaluating pain. Analogue for evaluating pain. Anesth 1976;31:1191-1198.
Moorf M, Khan SA, Jain D, Khan RM, Maroof SM. Evaluation of effect of dexmedetomidine in reducing shivering following epidural anesthesia. Anesthesiology 2004;101:495.
Kaya FN, Yavascaoglu B, Turker G, Yildirim A, Gurbet A, Mogol EB, et al. Intravenous dexmedetomidine, but not midazolam, prolongs bupivacaine spinal anesthesia. Can J Anaesth 2010;57:39-45