Cardiovascular Manifestations in Post Covid-19
Main Article Content
Abstract
BACKGROUND
COVID-19 is a pandemic which initially started in Wuhan, China and is still not under control worldwide. Because of evident spread in the many countries and increased death tolls WHO declared COVID-19 as a public health emergency on January 30 2020. Following recovery from COVID-19 many individuals have developed complications like clinical and sub clinical myocarditis, arrhythmias, pericarditis & pericardial effusion, heart failure and pulmonary embolism. So it is important to follow up with those patients who recovered from COVID-19 regularly for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the cardiac status of the patient who recovered from post COVID-19 by electrocardiography.
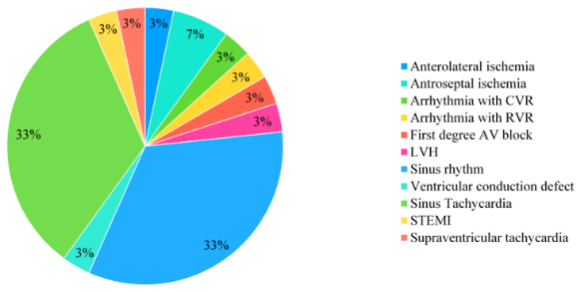
PATIENTS AND METHODS
This cross-sectional study was comprising of 30 patients who were recovered from COVID-19 was selected as study subjects based on convenient sampling. History of symptoms, events following hospitalisation, use of anti-coagulants was elicited in the study participants followed by complete clinical evaluation and their cardiac status was assessed by electrocardiography, levels of CRP and D-dimer during the recovery phase was noted. Association of ECG with levels of CRP and D-dimer, presence/absence of symptoms are studied and compared.
RESULTS:
Out of 30 patients we had no significant outcome but there is enough finding which has to be evaluated and followed with regular intervals to avoid the serious complications. So further highlights are need for a multifactorial analysis in more number with variable comparative factors to asses the prognosis in post-COVID-19.
CONCLUSION:
Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in post COVID-19 does not depend on one individual factor. It is multifactorial, hence consideration of other factors, long term follow up, multi system approach with more number of samples are needed for further analysis and interpretation.
Article Details
References
Huang Y. The Sars Epidemic And Its Aftermath In China: A Political Perspective. National Academies Press (US) (2004). Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92479/ (accessed May 04, 2020).Google Scholar
McCloskey B, Heymann DL. SARS to novel coronavirus–old lessons and new lessons. Epidemiol Infect. (2020) 148:e22. doi: 10.1017/S0950268820000254PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
https://covid19.who.int/region/searo/country/in
JAMA.2020;324(17):17231724.doi:10.1001/jama.2020.19719
Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, Wang B, Xiang H, Cheng Z, Xiong Y, Zhao Y, Li Y, Wang X, Peng Z. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020 Mar 17;323(11):1061-1069. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Huang L, Zhang C, Liu S, Zhao P, Liu H, Zhu L, Tai Y, Bai C, Gao T, Song J, Xia P, Dong J, Zhao J, Wang FS. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Apr;8(4):420-422. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Zheng YY, Ma YT, Zhang JY, Xie X. COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020 May;17(5):259-260. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Shi Y, Wang Y, Shao C, Huang J, Gan J, Huang X, Bucci E, Piacentini M, Ippolito G, Melino G. COVID-19 infection: the perspectives on immune responses. Cell Death Differ. 2020 May;27(5):1451-1454. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Driggin E, Madhavan MV, Bikdeli B, Chuich T, Laracy J, Biondi-Zoccai G, Brown TS, Der Nigoghossian C, Zidar DA, Haythe J, Brodie D, Beckman JA, Kirtane AJ, Stone GW, Krumholz HM, Parikh SA. Cardiovascular Considerations for Patients, Health Care Workers, and Health Systems During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 May 12;75(18):2352-2371. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Qin C, Zhou L, Hu Z, Zhang S, Yang S, Tao Y, Xie C, Ma K, Shang K, Wang W, Tian DS. Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Jul 28;71(15):762-768. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Xiong TY, Redwood S, Prendergast B, Chen M. Coronaviruses and the cardiovascular system: acute and long-term implications. Eur Heart J. 2020 May 14;41(19):1798-1800. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Lee D.W., Gardner R., Porter D.L. Current concepts in the diagnosis and management of cytokine release syndrome. Blood. 2014;124:188–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lin L, Xu Y-J, He D-P, Han Y, Tang G-H, Yang Z-M, Yu H, Lin ZX. A retrospective study on clinical features of and treatment methods for 77 severe cases of SARS. Am J Chin Med. 2003;31(6):821–839. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X03001521. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Saad M, Omrani AS, Baig K, Bahloul A, Elzein F, Matin MA, Selim MAA, Mutairi MA, Nakhli DA, Aidaroos AYA, Sherbeeni NA, al-Khashan HI, Memish ZA, Albarrak AM. Clinical aspects and outcomes of 70 patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection: a single-center experience in Saudi Arabia. Int J Infect Dis. 2014;29:301–306. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.09.003. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Babapoor-Farrokhran S, Gill D, Walker J, Rasekhi RT, Bozorgnia B, Amanullah A. Myocardial injury and COVID-19: possible mechanisms. Life Sci. 2020;253:117723. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117723. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
Zhand S, Saghaeian Jazi M, Mohammadi S, Tarighati Rasekhi R, Rostamian G, Kalani MR, Rostamian A, George J, Douglas MW Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 3; 21(15):. [PubMed] [Ref list]
Gopinathannair R, Merchant FM, Lakkireddy DR, Etheridge SP, Feigofsky S, Han JK, Kabra R, Natale A, Poe S, Saha SA, Russo AM J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2020 Nov; 59(2):329-336.[PubMed] [Ref list]
Li T, Cheng GS, Pipavath S, et al. The novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) complicated by pulmonary embolism and acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Med Virol 2020 May 29. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26068 [Epub ahead of print].
Porfidia A, Pula R. Venous thromboembolism in COVID-19 patients. J Thromb Haemost 2020 Apr 15. doi: 10.1111/jth.14842 [Epub ahead of print].
Leonard-Lorant I, Delabranche X, Severac F, et al. Acute pulmonary embolism in COVID-19 patients on CT angiography and relationship to D-dimer levels. Radiology 2020 Apr 23. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020201561 [Epub ahead of print].
Tang N, Bai H, Chen X, Gong J, Li D, Sun Z. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with clotpathy. J Thromb Haemost 2020;18:1094-9.