Co-Relation of Hypothyrodism with Triglyceride Level and Raised HDL Cholesterol
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: The cardiovascular system is negatively impacted by hyperthyroidism, but the majority of its positive effects on serum lipid levels. As a result, the focus of this review is on how thyroid disorders affect serum lipid levels, both overt and covert. A link between hypothyroidism and an increase in cardiovascular events has also been proposed. Subclinical hypothyroidism and increased carotid artery intima-media thickness, which may be a sign of early atherosclerosis, have been linked recently by two studies.
Aim and Objective: To study the co-relation of hypothyrodism with triglyceride level and raised HDL Cholesterol.
Methodology: At a tertiary care hospital in Ghaziabad, “total cholesterol (TC)”, “triglycerides (TG)”, “Very Low-Density Cholesterol (VLDL)”, “low density cholesterol (LDL)”, and “high density cholesterol (HDL)” were studied between the three study groups. Weight and waist size were reported in a semi-structured manner.
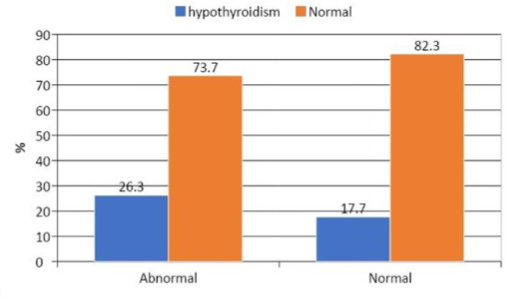
Result: “Hypothyroid was in 7% patients”. “Subclinical hypothyroidism” was in14% patients. When “total cholesterol was abnormal (26.3%) compared to normal (17.7%)”, the prevalence of hypothyroidism was greater. There was, however, no “statistically significant (p>0.05)” relation between the prevalence of hypothyroidism and total cholesterol.
Conclusion: The overwhelming body of research indicates that “HDL cholesterol levels” are normal to slightly raised in overt hypothyroidism, which results in an unfavourable “LDL cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio”.
Article Details
References
Bakker SJL, terMaaten JC, Popp-Snijders C, et al.: The relationship between thyrotropin and low density lipoprotein cholesterol is modified by insulin sensitivity in healthy euthyroid subjects. J ClinEndocrinolMetab 2001, 86:1206–1211.
Deshmukh V, Farishta F, Bhole M. Thyroid Dysfunction in Patients with MetabolicSyndrome: A Cross-Sectional, Epidemiological, Pan-India Study. Int J Endocrinol.2018.
Duntas LH, Orgiazzi J, Brabant G. The interface between thyroid and diabetes mellitus. ClinEndocrinol (Oxf) 2011;75(1):1-9
Elder J, McLelland A, O’Reilly DS, Packard CJ, Series JJ, Shepherd J, et al. The relationship between serum cholesterol and serum thyrotropin, thyroxine and tri iodothyronine concentrations in suspected hypothyroidism. Ann ClinBiochem 1990;27(Pt 2):110 3.
Kota S. K., Sarangi J., Jali S. N., Meher L. K., and Raveendranathan S. K.Prevalence ofhypothyroidism in patients withmetabolic syndrome. Thyroid Research and Practice2013;10(2): 6064.
Martinez-Triguero ML, Hernandez-Mijares A, Nguyen TT, et al.: Effect of thyroid hormone replacement on lipoprotein(a), lipids, and apolipoproteins in subjects with hypothyroidism. Mayo ClinProc 1998, 73:837–841. This study demonstrated the lipid effects of overt hypothyroidism and the effects of L-thyroxine therapy.
Mooradian AD. Dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat ClinPractEndocrinolMetab 2009; 5:150 9.
Müller B, Zulewski H, Huber P, et al.: Impaired action of thyroid hormone associated with smoking in women with hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med 1995, 333:964–969.
O’Brien T, Dineen SF, O’Brien PC, Palumbo PJ: Hyperlipidemia in patients with primary and secondary hypothyroidism. May ClinProc 1993, 68:860–866
O’Brien T, Dinneen SF, O’Brien PC, Palumbo PJ. Hyperlipidemia in patients with primary and secondary hypothyroidism. Mayo ClinProc 1993;68:860 6.
Packard CJ, Shepherd J, Lindsay GM, et al.: Thyroid replacement therapy and its influence on postheparin plasma lipases and apolipoprotein-B metabolism in hypothyroidism. J ClinEndocrinolMetab 1993, 76:1209–1216.
Perros P, McCrimmon RJ, Shaw G, Frier BM. Frequency of thyroid dysfunction in diabetic patients: Value of annual screening. Diabet Med 1995;12:622 7.
Senthil N., Thomas S., Santosh P. et al. A study ofprevalence of thyroid dysfunction inpatientswithmetabolicsyndrome.InternationalJournalofResearchinMedicalSciences2015; 3:31713176.
ShanthaG.P.,KumarA.A.,JeyachandranV.etal.Associationbetweenprimaryhypothyroidism and metabolic syndromeand the role of C reactive protein: a cross-sectionalstudyfromSouthIndia.ThyroidResearch2009; 2(1)
Staub JJ, Althaus BU, Engler H, Ryff AS, Trabucco P, Marquardt K, et al. Spectrum of subclinical and overt hypothyroidism: Effect on thyrotropin, prolactin, and thyroid reserve, and metabolic impact on peripheral target tissues. Am J Med 1992;92:631 42.
Thyroxine concentrations are associated with differing metabolic markers in euthyroid subjects. Eur J Endocrinol 2010;162(3);273-278
VelayuthamK.,SelvanS.S.A.,andUnnikrishnanA.G.PrevalenceofthyroiddysfunctionamongyoungfemalesinaSouthIndianpopulation.IndianJournalofEndocrinologyandMetabolism 2015; 19(6): 781784