A Rare Case Study of BRASH Syndrome
Main Article Content
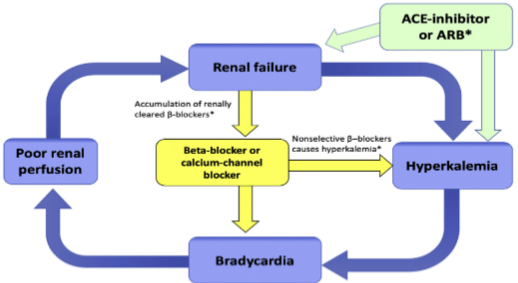
Abstract
BRASH syndrome in a combination of clinical findings resulting in patients with baseline renal failure on long term AV nodal blocking agents. Our case is a patient on long term AV nodal blocker who came with complaints of light headedness and further was diagnosed as BRASH syndrome. Initially the patient's will be started on intravenous fluids, administration of calcium gluconate, intravenous dextrose and insulin.
Article Details
References
Simmons T, Blazar E: Synergistic bradycardia from beta blockers,hyperkalemia, and renal failure. J Emerg Med. 2019, 57:41-44. 10.1016/j.jemermed.2019.03.039
Arnsdorf MF, Schreiner E, Gambetta M, Friedlander I, Childers RW: Electrophysiological changes in the canine atrium and ventricle during progressive hyperkalaemia: electrocardiographical correlates and the in vivo validation of in vitro predictions. Cardiovasc Res. 1977, 11:409-418. 10.1093/cvr/11.5.409
Aziz EF, Javed F, Korniyenko A, et al.: Mild hyperkalemia and low eGFR a tedious recipe for cardiac disaster in the elderly: an unusual reversible cause of syncope and heart block. Heart Int. 2011, 6:12.
Juvet T, Gourineni VC, Ravi S, Zarich SW: Life-threatening hyperkalemia: a potentially lethal drug combination. Conn Med. 2013, 77:491-493
Argulian E: An unusual case of syncope . Am J Med. 2009, 122:636-638.10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.03.017
PulmCrit. BRASH syndrome: bradycardia, renal failure, AV blocker, shock, hyperkalaemia .(2016). Accessed: February 15, 2020: https://emcrit.org/pulmcrit/brash-syndromebradycardia-renal-failure-av-blocker-shock-hyperkalemia/.
Jefferson AL, Poppas A, Paul RH, Cohen RA. Systemic hypoperfusion is associated with executive dysfunction in geriatric cardiac patients. Neurobiol Aging. 2007;28:477–83.