Drug Induced Acute Pancreatitis and Diabetic Ketoacidosis in A Non-Diabetic, Bipolar Patient
Main Article Content
Abstract
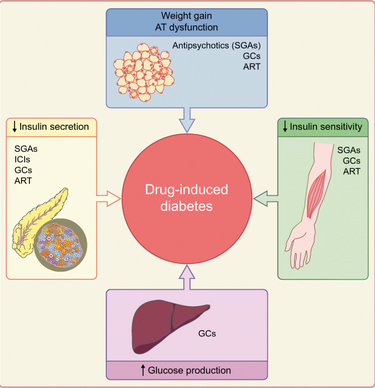
A young non diabetic male patient on treatment with sodium valproate for hypomanic phase of bipolar disorder, developed diabetic ketoacidosis and acute pancreatitis which is transient in nature after starting the patient on haloperidol and chlorpromazine medications. Patient condition improved and resolved completely with his sugar levels coming back to normal in six weeks of time. Acute pancreatitis and diabetic ketoacidosis manifesting combinedly is a very rare occurrence. This condition can be seen in patients who are on antipsychotic medications like sodium valproate, haloperidol and chlorpromazine. Hence it is important to monitor levels of blood glucose in patients who are on antipsychotic medications. This regular monitoring helps in preventing complications related to hyperglycaemia.
Article Details
References
Association of diabetic ketoacidosis and acute pancreatitis: observations in 100 consecutive episodes of DKA - Nair S, Yadav D, Pitchumoni CS.
Chlorpromazine induced diabetes mellitus. - J Association of physicians of India, Aruna, Paulose KP
Pancreatitis associated with Valproic acid: a review of the literature, Pharmacotherapy - Chapman SA, Waksman GP, Patterson BD.
Bai YM, Su TP, Chen MH, Chen TJ, Chang WH. Risk of developing diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidaemia among patients with bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, and schizophrenia: a 10-year nationwide population-based prospective cohort study. J Affect Disord. 2013; 150:57–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2013.02.019.
Calkin CV, Gardner DM, Ransom T, Alda M. The relationship between bipolar disorder and type 2 diabetes: more than just co-morbid disorders. Ann Med. 2013; 45:171–181. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2012.687835.
Calkin CV, Ruzickova M, Uher R, Hajek T, Slaney CM, Garnham JS, et al. Insulin resistance and outcome in bipolar disorder. Br J Psychiatry. 2015; 206:52–57. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.114.152850.
Atypical antipsychotics and diabetic ketoacidosis: a review.
Guenette MD, Hahn M, Cohn TA, Teo C, Remington GJ. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Mar;226(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-2982-3. Epub 2013 Jan 24
Development of acute pancreatitis caused by sodium valproate in a patient with bipolar disorder on haemodialysis for chronic renal failure: a case report.
Okayasu H, Shinozaki T, Osone A, Ozeki Y, Shimoda K.BMC Psychiatry. 2014 Mar 29; 14:93. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-14-93.
Acute pancreatitis and diabetic ketoacidosis in non-diabetic person while on treatment with sodium valproate, chlorpromazine and haloperidol V D Laghate , S B Gupta