Risk Perception of Outsourcing of Medicine in Indian Pharmaceutical Industry
Main Article Content
Abstract
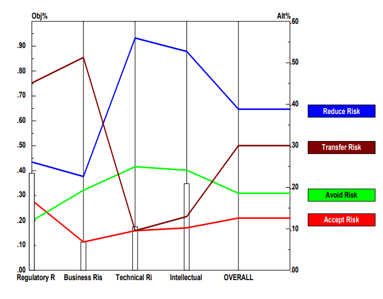
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly outsourcing their supply chain activities due to significant pressure to cut R&D expenses. The ability to outsource parts of one's global supply chain can be seen as a strategic competitive weapon rather than a cost-cutting measure, as it can allow for more adaptability in production, greater satisfaction of the ever-changing needs of the ultimate consumers, lower fixed costs, and better leverage of market position. For this reason, outsourcing the global supply chain has become a need for pharmaceutical companies to remain competitive. It helps businesses to make far more use of their primary competencies and resources than is possible via other methods. When implemented properly, global supply chain outsourcing solutions may increase returns on capital, lower risk, increase flexibility, and help businesses be more responsive to the needs of their customers and shareholders. Despite widespread recognition of the appealing advantages of global outsourcing, many of the inherent hazards have been largely ignored. Regulatory risk, operational risk, technological risk, and corporate social responsibility risk are only some of the dangers associated with outsourcing the pharmaceutical supply chain. Avoidance, reduction (mitigation), transfer, and acceptance are all methods of supply chain risk management that may be used to lessen an organization's vulnerability to supply chain outsourcing risks.
Article Details
References
Majd Mohammad Omoush (2020), “Investigation the Relationship Between Supply Chain Management Activities and Operational Performance: Testing the Mediating Role of Strategic Agility-A Practical Study on the Pharmaceutical Companies”, International Business Research, Volume 13.
Ward R., Hargaden V. (2019) An Exploratory Assessment of Risk and Resilience in Pharmaceutical Supply Chains. In: Barbosa-Povoa A., Jenzer H., de Miranda J. (eds) Pharmaceutical Supply Chains — Medicines Shortages. Lecture Notes in Logistics. Springer, Cham.
Wong WP., Soh KL. (2019) Review of Pharmaceutical Sea Freight and Malaysian Third-Party Logistics Service Providers: A Supply Chain Perspective. In: Barbosa-Povoa A., Jenzer H., de Miranda J. (eds) Pharmaceutical Supply Chains — Medicines Shortages. Lecture Notes in Logistics. Springer, Cham.
Prabal Chakraborty (2020), “Indian Pharmaceuticals Industry in Global Scenario: An Appraisal”, Journal of Health Management, https://doi.org/10.1177/0972063420937939.
Valentin Steinwandter, Christoph Herwig (2019), “Provable Data Integrity in the Pharmaceutical Industry Based on Version Control Systems and the Blockchain”, doi: 10.5731/pdajpst.2018.009407
Christine Xia, Ajay Gautam (2015), “Biopharma CRO industry in China: landscape and opportunities”, Drug Discvery, DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2015.02.007.
DAVID TAYLOR (2016), “The Pharmaceutical Industry and the Future of Drug Development”, DOI:10.1039/9781782622345-00001.
El Mokrini, E. Dafaoui, A. Berrado, A. El Mhamedi (2016), “An approach to risk Assessment for Outsourcing Logistics: Case of Pharmaceutical Industry”, International Federation of Automatic Control, Volume 49.
B Karunakar (2016), “Indian Pharmaceutical Industry: The Changing Dynamics”, Int. Journal of Management Research & Business Strategy, Volume 5.
S. van Niekerk, W. Niemann, T. Kotzé& K. Mocke (2017), “Supply chain security orientation in the pharmaceutical industry”, Southern African Business Review, Volume 21