Beneficial Effect on Diabetic Nephropathy by Monotherapy as Well as their Combinations Therapy
Main Article Content
Abstract
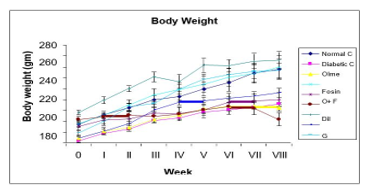
Intracellular calcium has been found to play a major role in the development of renal damage in diabetic kidneys, and oxidative stress has been connected to diabetic nephropathy. Calcium antagonism may postpone diabetes-related renal deterioration. This research compared the effectiveness of monotherapy and combination treatment for treating diabetic nephropathy in people with type 2 diabetes that was produced in the lab. Experimentally induced type 2 diabetes in rats was evaluated using a variety of treatment regimens, including fosinopril (ACE Inh), olmesartan (ARB), glimepiride (SU), pioglitazone (TZDs), and diltiazem (CCB) alone and in combination. Due to their complementary mode of action and synergistic benefits, combination treatments are preferable to monotherapies for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy, as shown by the findings of the aforementioned studies.
Article Details
References
Ozturk, Savas &Aydın, Zeki &Gursu, Meltem&Abanoz, Emre & Uzun, Sami & Karadag, Serhat&Yenigun, Mustafa &Kazancioglu, Rumeyza. (2012). Short Term Effects of Diltiazem on Renal Functions: A Controlled Clinical Study. Turkish Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 21. 130-135. 10.5262/tndt.2012.1002.05.
Elgendy, Salwa. (2012). Study of the effect of simvastatin, pioglitazone, diltiazem and pentoxifylline on the development and progression of nephropathy in streptozotocin induced diabetic rat model.
Kim, S.; Yu, Y.M.; Kwon, J.; Yoo, H.; Jung, S.H.; Lee, E. Calcium Channel Blocker-Associated Chyloperitoneum in Patients Receiving Peritoneal Dialysis: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1333.
Verma, S., Abhishek, A., Mishra, O. P., Singh, A., & Prasad, R. (2021). Comparison of Efficacy of First Haemodialysis Session for Correction of Metabolic Disturbances in Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease in Children. Journal of Nepal Paediatric Society, 41(1), 35–41.
Giralt-López, A.; Molina-Van den Bosch, M.; Vergara, A.; García-Carro, C.; Seron, D.; Jacobs-Cachá, C.; Soler, M.J. Revisiting Experimental Models of Diabetic Nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3587.
Carrara, F.; Azzollini, N.; Nattino, G.; Corna, D.; Villa, S.; Cerullo, D.; Zoja, C.; Abrante, B.; Luis-Lima, S.; Porrini, E.; et al. Simplified method to measure glomerular filtration rate by Iohexol plasma clearance in conscious rats. Nephron 2016, 133, 62–70.
Viswanathan, G.; Upadhyay, A. Assessment of Proteinuria. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2011, 18, 243–248
Burke, K.; Reifsnyder, P. Protocol for Albuwell M kit: Murine Microalbuminuria ELISA by Exocell Inc., 2008 Animal Models of Diabetic Complications Consortium (AMDCC).
Jaffe, M. Ueber den Niederschlag, welchen Pikrinsäureimnormalen Harnerzeugt, und übereineneue Reaction des Kreatinins. Z. Physio.l Chem. 1886, 10, 391–400
Tervaert, T.W.C.; Mooyaart, A.L.; Amann, K.; Cohen, A.H.; TerenceCook, H.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Ferrario, F.; Fogo, A.B.; Haas, M.; De Heer, E.; et al. Pathologic classification of diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 556–563.
Ziyadeh, F.N.; Hoffman, B.B.; Han, D.C.; Iglesias-De La Cruz, M.C.; Hong, S.W.; Isono, M.; Chen, S.; McGowan, T.A.; Sharma, K. Long-term prevention of renal insufficiency, excess matrix gene expression, and glomerular mesangial matrix expansion by treatment with monoclonal antitransforming growth factor-β antibody in db/db diabetic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8015–8020.
Ayo, S.H.; Radnik, R.A.; Glass, W.F.; Garoni, J.A.; Rampt, E.R.; Appling, D.R.; Kreisberg, J.I. Increased extracellular matrix synthesis and mRNA in mesangial cells grown in high-glucose medium. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 260, F185–F191.
Stevens, M.; Oltean, S. Assessment of kidney function in mouse models of glomerular disease. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 2018, 1–10
Sheehan, S.M.; Korstanje, R. Automatic glomerular identification and quantification of histological phenotypes using image analysis and machine learning. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 315, F1644–F1651.
Rangan, G.K.; Tesch, G.H. Quantification of renal pathology by image analysis (Methods in Renal Research). Nephrology 2007, 12, 553–558.