Growth Performance and Immune Response of Oreochromis Niloticusl L. with the Effect of Marine Macroalgal Fish Feed: Halymenia Floresii (Clemente) C.Ag.
Main Article Content
Abstract
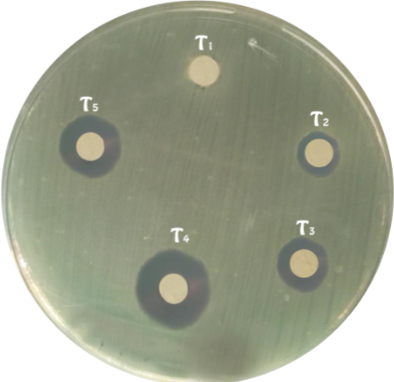
Fish aquaculture has currently taken a pre-eminent position. The demanding situations confronted via the means of fish farmers, the cost of the fish feed and quality management of fish. Marine macroalgae are embedded with a variety of biochemical compounds that could assist as a shield in opposition to infectious diseases. This study was designed to analyze the impact of the seaweed Halymenia floresii in growth promotion and immune response in Oreochromis niloticusL as an alternate protein source in replacing a fish meal. The feed proximity includes the analysis of total carbohydrates, total fiber, total proteins, total lipids, moisture and ash. The experimental feed regimens were categorized as T1 (Control), T2 (10%), T3 (20%), T4 (30%) and T5 (40%) and enhanced with the consistent percentage of algal powder throughout the study period. The growth parameters such as average weight gain, average length, specific growth rate and feed conversion ratio (FCR) were observed at the 60thday of the rearing period. Red blood cells (RBC), White blood cells (WBC), hemoglobin (Hb), hematocrit (HCT), Mean corpuscle volume (MCV), Mean corpuscle hemoglobin (MCH) and Mean corpuscle hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) were all assessed to evaluate the immunological response of Oreochromis niloticus. Halymenia floresii also efficient against Vibrio cholera. The consequences of this research work revealed that Halymenia floresii has positive impact on the growth and immune system of Oreochromis niloticus.